Proper Way to Start Dating Again After Herpes Diagnosis
Researchers in The Netherlands and Germany have warned that Pfizer-BioNTech's coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-nineteen) vaccine induces circuitous reprogramming of innate allowed responses that should be considered in the development and use of mRNA-based vaccines.
Jorge Domínguez-Andrés and colleagues say that while the vaccine has been shown to be up to 95% constructive in preventing infection with astringent acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-ii) and subsequent COVID-xix, piddling is known nearly the broad furnishings the vaccine may have on the innate and adaptive immune responses.
In the current written report (not peer-reviewed*), the enquiry team from Radboud University Medical Center and Erasmus MC in the Netherlands, and the Helmholtz-Centre for Infection Research (HZI), Hannover Medical Schoolhouse (MHH), and the University of Bonn, in Frg, confirmed the efficacy of BNT162b2 vaccination at inducing constructive humoral and cellular immunity confronting several SARS-CoV-2 variants.

However, they as well showed that the vaccine altered the product of inflammatory cytokines by innate immune cells post-obit stimulation with both specific (SARS-CoV-2) and non-specific (viral, fungal and bacterial) stimuli.
Following vaccination, innate immune cells had a reduced response to toll-similar receptor 4 (TLR4), TLR7 and TLR8 – all ligands that play an important role in the allowed response to viral infection.
Neta and colleagues also establish that cytokine responses to fungi were increased following vaccination.
The mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine induces complex functional reprogramming of innate immune responses, which should be considered in the development and use of this new class of vaccines," writes the team.
A pre-impress version of the inquiry paper is bachelor on the medRxiv* server. A preprint is a version of a scholarly or scientific newspaper that precedes formal peer review and publication in a peer-reviewed scholarly or scientific periodical.
The accelerated development of new vaccine technologies
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began in tardily December 2019, researchers beyond the globe have been racing to develop vaccines to help combat the global healthcare crisis.
The scale of the pandemic has led to the accelerated evolution of new mRNA-based vaccines, the first of which to be registered was the BNT162b2 vaccine from Pfizer-BioNTech.
This vaccine is based on a lipid nanoparticle–formulated, nucleoside-modified mRNA that encodes the fasten protein of the SARS-CoV-two strain that was isolated early in the pandemic in Wuhan, Communist china.
The spike protein is the principal construction the virus uses to infect host cells, and its receptor-binding domain (RBD) is a primary target of neutralizing antibodies following natural infection or vaccination.
Several phase three trials have shown that BNT162b2 elicits wide humoral (antibody) and cellular responses that protect against COVID-19. However, many challenges remain while this and other mRNA-based vaccines are rolled out globally, with the emergence of new variants beingness of detail business organization.
The variants that have emerged in the Britain (B.1.1.7 lineage), South Africa (B.ane.351), and Brazil (P.ane) comprise multiple mutations in the spike that could touch on disease severity, viral transmissibility, and vaccine effectiveness.
The capacity of BNT162b2 to induce constructive humoral and cellular immunity against the new SARS-CoV-2 variants is only at present offset to be understood," says Domínguez-Andrés and colleagues.
Furthermore, an unexplored area is whether BNT162b2 vaccination has long-term effects on innate immune responses:
This could be very relevant in COVID-nineteen, in which dysregulated inflammation plays an important part in the pathogenesis and severity of the illness," writes the squad. "Multiple studies have shown that long-term innate allowed responses tin can be either increased (trained immunity) or down-regulated (innate allowed tolerance) after certain vaccines or infections."
What did the researchers do?
The researchers showed that one dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine induces high concentrations of anti-spike and anti-fasten RBD antibodies, while a second dose three weeks later elicits even higher levels.
All the mail-vaccine serum samples tested effectively neutralized the B.i.1.7 variant, just 37.5% showed decreased neutralizing activity against the B.1.351 variant.
These data support the evidence that B.1.351, and possibly other variants, may be able to escape vaccine-induced humoral immunity to a certain extent," say the researchers.
What about the cellular response?
Vaccination with BNT162b2 has been reported to activate SARS-CoV-two-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and to increment the production of immune-modulatory cytokines such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ).
Domínguez-Andrés and colleagues, therefore, assessed the secretion of IFN-γ from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in response to unlike SARS-CoV-ii strains earlier and after BNT162b2 vaccination.
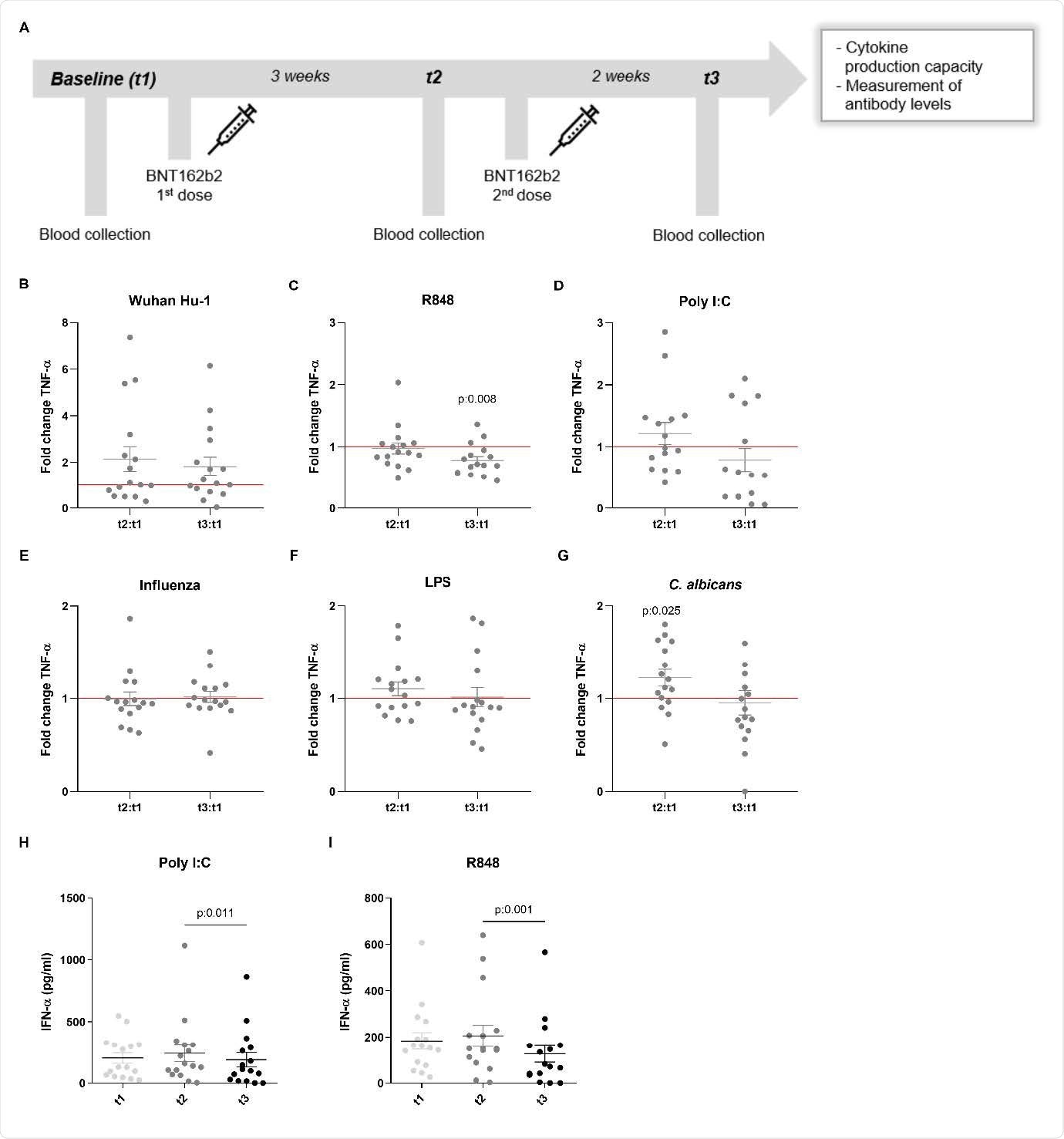
TNF-α and IFN-α production in response to heterologous stimuli in PBMCs isolated from vaccinated subjects. (A) Description of the report: vaccination and claret collection days. (B-1000) Fold change values of TNF-α product are calculated individually for each bailiwick by division of t2:t1 and t3:t1. Data are presented equally fold changes ± SEM (n=15-sixteen) and analysed past Wilcoxon'due south matched-pairs signed-rank test comparing each ratio to t1=1 (blood-red line). (H-I) IFN-α production (pg/ml) at t1, t2 and t3. Data are presented as cytokine concentration ± SEM (n=fifteen-16) and analysed by Wilcoxon's matched-pairs signed-rank test.
Vaccination increased IFN-γ production past at least 50% in 37.5% of the samples stimulated with the standard SARS-CoV-2 strain, in 50% stimulated with the B.i.ane.7 or B.1.351 variant, but just in xviii.8% of samples stimulated with the Bavarian variant.
These findings argue that BNT162b2 vaccination induces better humoral than cellular immune responses," say the researchers.
Cytokine responses to certain stimuli were reduced post-obit vaccination
Interestingly, BNT162b2 vaccination decreased IFN-γ production post-obit stimulation with the TLR7 and TLR8 agonist R848. The TLR7 and TLR8 ligands are key players in the immune response to viral infection.
Vaccination also decreased production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis cistron-α and interleukin-1β following stimulation with either the standard SARS-CoV-2 strain or unlike Price-similar receptor ligands.
In contrast, responses to the fungal pathogen Candida albicans were higher after vaccination.
In improver, the product of the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1Ra was reduced in response to Toll-similar receptor iv and C. albicans. This also suggests a shift towards increased inflammatory responses to fungi following vaccination, say the researchers.
These results collectively demonstrate that the effects of the BNT162b2 vaccine go beyond the adaptive allowed arrangement," writes the team. "The BNT162b2 vaccine induces reprogramming of innate immune responses as well, and this needs to exist taken into account."
What do the authors suggest?
The researchers say that in combination with strong adaptive immune responses, the reprogramming of innate responses could either contribute to a more balanced inflammatory reaction to SARS-CoV-ii infection or a weakened innate allowed response.
The consequence of the BNT162b2 vaccination on innate immune responses could also interfere with the responses to other vaccinations, adds the team.
Our findings need to be confirmed by conducting larger accomplice-studies with populations with diverse backgrounds, while further studies should examine the potential interactions betwixt BNT162b2 and other vaccines," concludes Domínguez-Andrés and colleagues.
* Important Notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practise/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
Journal reference:
- Domínguez-Andrés J, et al. The BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine confronting SARS-CoV-2 reprograms both adaptive and innate immune responses. medRxiv, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/x.1101/2021.05.03.21256520, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/ten.1101/2021.05.03.21256520v1
macdonaldhougmenseed.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.news-medical.net/news/20210510/Research-suggests-Pfizer-BioNTech-COVID-19-vaccine-reprograms-innate-immune-responses.aspx
Post a Comment for "Proper Way to Start Dating Again After Herpes Diagnosis"